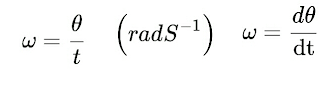centripetaceleration and centripetal force
By ka cheung chan
Linear velocity
The vector of any mass is equal to the tangant the radius. Thus although the magnitute of the velocity does not change, its direction change toward the centre. Velocity changes over time. There is an acceleration.
Centripetacceleration
Va is the instant velocity of position a whereas Vb is that of position b. After a short interval of time, a move to b and the vector changed delta v. Owing to the angle change is so small that delta v can be seem as perpendicular to both Va and Vb. Hence, that is the direction to the centre.
Centripetal force
According to Newton's second law